3 Ligaments Of The Hip. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Dislocation of the hip joint. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest.
3 Ligaments Of The Hip - Pcl Reconstruction Rehabilitation Online Course:
Hip Ligaments Artwork Photograph By Science Photo Library. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
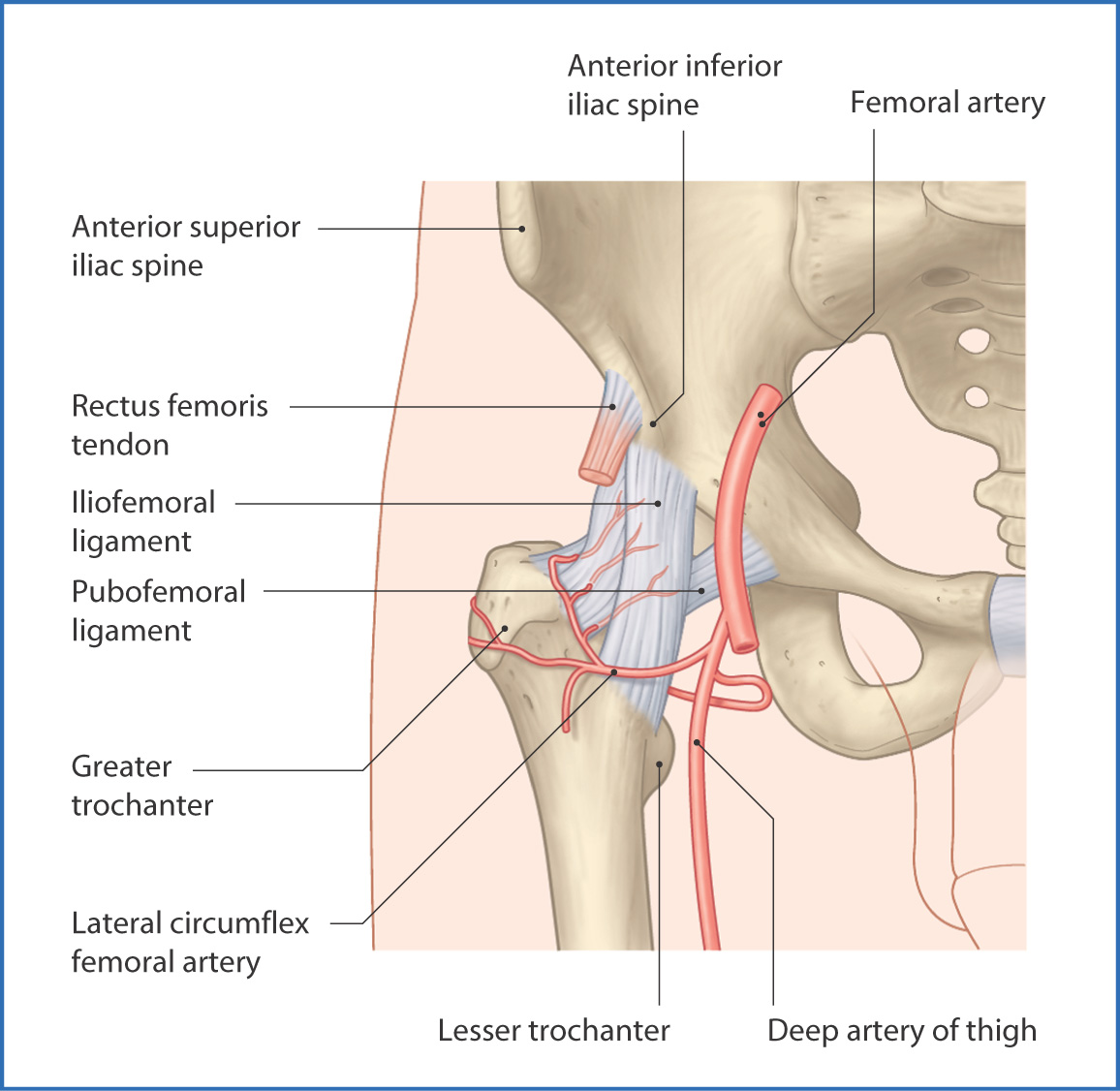
Function of the iliofemoral ligament.
The ischiofemoral ligament is located posteriorly; Dislocation of the hip joint. Pcl reconstruction rehabilitation a framework for posterior cruciate. The hip bone, or coxal bone, forms the pelvic girdle portion of the pelvis. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The femur is the upper leg bone or thigh. Annular ligament of the hip, transverse acetabular, iliofemoral. Each hip bone consists of the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. 6, cotyloid ligament around the acetabulum; The support provided by the inguinal ligament is important to maintaining the flexibility of the hip region while allowing vital blood and nerve supply to the leg. If orl is tight, resting finger position is dip extended, pip flexed. The paired hip bones are the large, curved bones that form the lateral and anterior also spanning the sacrum and hip bone are two additional ligaments. The hip bones, connected by the pubic symphysis, and the vertebrae, connected by intervertebral discs, are two examples of symphyses. In anatomy, a ligament is a band or sheet of strong fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones, or to cartilage, or supports an organ, such as the spleen, uterus, or eyeball. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. The iliofemoral ligament, sometimes referred to as the y ligament of bigelow, attaches to the anterior. Two ligaments reinforce the hip anteriorly: The ischiofemoral ligament is located posteriorly; Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. ► iliofemoral ligament (1 f). The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The pelvic cavity is a space located within the pelvic girdle that contains parts of the gastrointestinal. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Reconstruction of oblique retinacular ligament used to treat swan neck deformity. The top countries of suppliers are india, china, and india, from. Category for files related to ligaments of the hip. It's thought that babies in a normal. Hip dysplasia or ddh is normally diagnosed in babies however it can develop later on. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck.
Anatomyexpert Hip Joint And Ligaments Structure Detail - Reconstruction Of Oblique Retinacular Ligament Used To Treat Swan Neck Deformity.
Ligaments Of The Hip A Drawing Of The Anterior Hip Shows The Download Scientific Diagram. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Dislocation of the hip joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae).
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy : Distally, It Attaches To The Intertrochanteric Line Anteriorly And The Femoral Neck.
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Dislocation of the hip joint. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck.
Ligaments Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis . This is an online quiz called ligaments of the hip.
Anatomy And Physiology Designed For Academies And Families Fig 41 The Ligaments Of The Pelvis And Hip Joint 1 The Lower Part Of The Anteriordgament Of The Vertebrae 2 A. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Dislocation of the hip joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest.
Hip Joint Rania Gabr Ppt Video Online Download . ► Iliofemoral Ligament (1 F).
Preventing Yoga Injuries I Love Yoga Anatomy. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Dislocation of the hip joint. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally.
Hip And Groin Injuries Unraveling The Mystery : Related Online Courses On Physioplus.
Capuslar Ligaments Of The Hip Download Scientific Diagram. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament.
Hip Joint Model With Sacrum And Ligaments On Stand : Hips Braces Suporter Patella Stabilizer Knee Strap Brace Support For Hip.
Fg Anatomy G49 Joints Of The Lower Extremity Anatomy Unit 6 Flashcards Memorang. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Dislocation of the hip joint. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb:
The Ligaments Of The Hip Joint Capsule Have A Lower Elasticity And Less Download Scientific Diagram - Bones Of The Hip Joint.
Human Hip Ligaments Stock Image F015 7785 Science Photo Library. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
Anatomyexpert Hip Joint And Ligaments Structure Detail : The Femur Is The Upper Leg Bone Or Thigh.
Musculoskeletal Pelvic Anatomy Sciencedirect. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Dislocation of the hip joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
Hip Joint Treatment Sydney Hip Ligaments Treatment Sydney : Each Hip Bone Consists Of The Ilium, Ischium, And Pubic Bone.
Hip Joint Bones Movements Muscles Kenhub. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Dislocation of the hip joint. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum.
Quiz 3 Material Hip Joint Flashcards Quizlet . In Anatomy, A Ligament Is A Band Or Sheet Of Strong Fibrous Connective Tissue That Connects Bones To Other Bones, Or To Cartilage, Or Supports An Organ, Such As The Spleen, Uterus, Or Eyeball.
Hip And Ligaments Flashcards Quizlet. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Dislocation of the hip joint. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency.